Omnidata: A Scalable Pipeline for Making Multi-Task Mid-Level Vision Datasets from 3D Scans
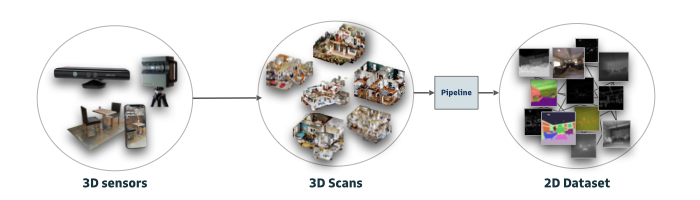 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
The Omnidata annotator is a pipeline to resample comprehensive 3D scans from the real-world into static multi-task vision datasets. Because this is resampling is parametric, we can control or steer datasets. This enables interesting lines of research (such as looking into the effects of these different parameters). And the resampled data can be used to train strong and robust vision models (results, demo). For example, we create a starter dataset of 14 million images sampled from 2000 scanned spaces. Familiar architectures trained on a generated starter dataset reached state-of-the-art performance on multiple common vision tasks and benchmarks, despite having seen no benchmark or non-pipeline data. The depth estimation network outperforms MiDaS and the surface normal estimation network is the first to achieve human-level performance for in-the-wild surface normal estimation (at least according to one metric on the OASIS benchmark). With 3D scanners becoming increasingly prevalent (e.g. on iPhones and iPads), we expect 3D scans to be a rich source of data in the future. We’re therefore open-sourcing everything in order to make it easier to do research with steerable datasets. The Dockerized pipeline with CLI and its (mostly Python) code, PyTorch dataloaders for the resulting data, the starter dataset, download scripts, and other utilities are available in the linked GitHub repos above.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code and math.